My Blog
Digging Deeper: The Art and Impact of Root Cause Analysis in IT
February 9, 2025
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is an essential process in IT operations, especially within the roles of Tier 2 and Tier 3 Application Support Analysts. RCA is not merely about identifying what went wrong; it is about understanding why it happened, how to prevent it in the future, and ensuring system reliability and efficiency.
The Impact on End Users and Production Applications
Effective RCA directly influences the stability and performance of production applications, which in turn affects end-user experience. When issues arise, end users face disruptions that can lead to decreased productivity, customer dissatisfaction, and potential financial losses. Application Support Analysts play a pivotal role in mitigating these risks by swiftly identifying the root cause of incidents and implementing long-term solutions rather than temporary fixes.
The Need for Consistency and Documentation
Consistency in performing RCA ensures that incidents are handled systematically, reducing the chances of recurring problems. A standardized approach allows teams to:
Maintain uniform investigation procedures across different incidents.
Facilitate knowledge sharing within and across support teams.
Ensure comprehensive documentation for future reference, aiding in quicker resolutions for similar issues.
Thorough documentation serves as an invaluable resource for trend analysis, helping organizations identify patterns that could indicate larger systemic issues.
Tidy Imports with Python
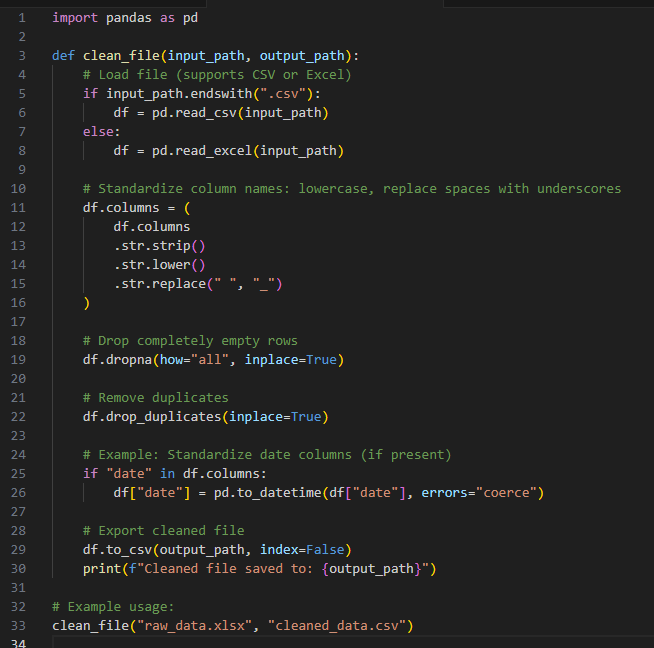
One of the most common challenges in data analysis and application support is dealing with messy, inconsistent files. Whether you’re working with spreadsheets, CSVs, or exports from a third-party system, raw files often come with quirks—extra spaces, inconsistent column names, duplicate rows, or unwanted formatting.
Recently, I created a small Python script to streamline this process. The script loads an incoming file, applies a few standardization steps, and outputs a clean version ready for use in reporting or system imports.
This script demonstrates the power of automation with Python. Instead of cleaning files manually each time, I can run this script and get consistent, reliable results. The benefits include:
Faster processing of incoming files.
Reduced human error.
A standard structure for downstream systems and reporting.
While this is a simple script, it can be extended with additional rules:
Validating data types (e.g., making sure IDs are numeric).
Mapping column names to standard labels.
Adding logging or error handling for production use.
In today’s data-driven workflows, automation like this can make a huge difference. A few lines of Python can save hours of manual cleanup—and ensure your data is always ready for analysis or system integration.
January 15, 2024
Safeguarding Data: The CIA Triad
In today’s digital world, data is both an asset and a liability. It powers decision-making, customer experiences, and innovation—but if mishandled, it can create risks ranging from compliance violations to full-scale breaches.
To manage these challenges, security professionals often rely on the CIA Triad:
Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability
Confidentiality: Ensuring that only authorized individuals can access information. This often involves authentication (e.g., passwords, multi-factor authentication) and encryption (both at rest and in transit).
Integrity: Protecting data from unauthorized modification, whether accidental or malicious. Integrity means the data you’re working with is accurate, reliable, and hasn’t been tampered with.
Availability: Ensuring data and systems are accessible when needed. Backups, redundancy, and disaster recovery planning all help maintain availability in the face of outages or cyberattacks.
This model provides a simple but powerful framework for understanding how to protect sensitive information and keep systems resilient.
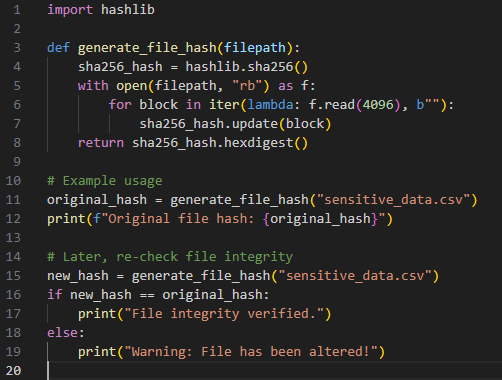
As an example, I created a Python snippet to verify whether a file has been altered by generating and checking its SHA-256 hash.
This simple technique can be applied to incoming data files, ensuring that what you import or share hasn’t been changed since its creation.
March 21, 2024
Beyond the Band-Aid: Why Root Cause Analysis Matters
Introduction: Why Root Cause Analysis Matters
In every system—whether it’s software, healthcare, or business ops—things go wrong. A form fails to load, a patient record disappears, a report returns incomplete data. Quick fixes patch the pain, but the same issue resurfaces… again. And again.
That’s where Root Cause Analysis (RCA) steps in—not to place blame, but to prevent recurrence and strengthen the system.
“You can’t fix what you don’t understand. And if you’re fixing the same thing twice, you probably didn’t fix the right thing.”
What Is Root Cause Analysis?
RCA is a structured method for identifying the underlying reason an issue occurred—not just the obvious symptom. It’s a cornerstone of:
Application support
Process improvement
Incident response
Quality assurance
Clinical risk analysis (in healthcare)
RCA is about learning, not finger-pointing. It creates a culture of curiosity, responsibility, and continuous improvement.
If your team dreads RCA reviews, it’s likely because they feel punished, not empowered.
August 3, 2024
The Role of Training and Continuous Improvement
Training is fundamental for Application Support Analysts to stay updated on best practices, tools, and methodologies related to RCA. Regular training sessions:
Enhance analytical skills required for effective problem-solving.
Introduce new technologies and techniques for more efficient RCA.
Promote a culture of continuous learning and improvement within the team.
Moreover, post-incident reviews and lessons learned sessions are critical. They provide opportunities for team members to discuss what went well, what didn’t, and how processes can be improved.
Collaboration and Communication
RCA is rarely a solo endeavor. It requires collaboration across different teams, including development, operations, and business stakeholders. Clear and transparent communication ensures that all parties are aligned on the incident’s impact, root cause, and corrective actions.
Conclusion
Root Cause Analysis is a cornerstone of effective IT support, particularly for Tier 2 and Tier 3 Application Support Analysts. By emphasizing consistency, thorough documentation, continuous training, and cross-functional collaboration, organizations can enhance their incident management processes, leading to more stable applications and improved end-user satisfaction. Ultimately, RCA is not just about fixing problems—it's about preventing them and driving long-term operational excellence.